magnetic properties of materials
magnetic properties of materials: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Hysteresis, Meissner Effect, Curie Temperature, Curie Law, Coercivity, Retentivity, Diamagnetic Substances, Paramagnetic Substances, Ferromagnetic Substances, Superconducting Magnets and, Magnetic Properties of Matter
Important Questions on magnetic properties of materials
Two blocks of different materials are placed in a uniform magnetic field . The magnetic field lines passing through the two blocks are represented as follows.
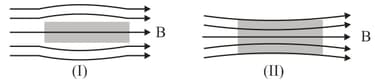
Identify the suitable values of relative permeability and magnetic susceptibility for the materials I and II.
Is Coercivity and Retentivity directly proportional?
Curie temperature is the temperature above which
When Superconductors, are heated above the critical temperature, they expel magnetic field and do not allow the magnetic field to penetrate inside them.
Explain meissner Effect
Meissner effect is strictly followed by
What is the Meissner effect?
In superconductivity the conductivity of a material becomes
The coils of a superconducting magnet are usually made of niobium _____ in a copper matrix.
In a superconductor, electricity will flow for a long time and then stop.
What are superconducting magnets?
The hysteresis loss in soft magnetic materials must be kept ______
Nickel shows ferromagnetic property at room temperature. If the temperature is increased beyond Curie temperature, then it will show
Which among the following is not an application of hard ferromagnetic material?
Identify two soft ferromagnetic materials.
List out some applications of hard and soft magnetic materials.
Iron is the best example for hard magnetic material.
What are hard and soft magnetic materials? Give examples.
The relative permeability of iron is . Its magnetic susceptibility is _____.
Explain origin of diamagnetism on the basis of its atomic structure.
